Polysaccharides
The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or as components of plant cell walls. Polysaccharides are very large polymers (long chains of molecules) composed of tens to thousands of monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic linkages. The three most abundant polysaccharides are starch, glycogen, and cellulose. These three are referred to as homopolymers because each yields only one type of monosaccharide (glucose) after complete hydrolysis. Heteropolymers may contain sugar acids, amino sugars, or noncarbohydrate substances in addition to monosaccharides. Heteropolymers are common in nature (gums, pectins, and other substances) but will not be discussed in detail in this textbook. The polysaccharides are not sweet tasting, and do not undergo mutarotation.
Starch
Starch is the most important source of carbohydrates in the human diet and accounts for more than 50% of our carbohydrate intake. It occurs in plants in the form of granules, and these are particularly abundant in seeds (especially the cereal grains) and tubers, where they serve as a storage form of carbohydrates. The breakdown of starch to glucose nourishes the plant during periods of reduced photosynthetic activity. We often think of potatoes as a “starchy” food, yet other plants contain a much greater percentage of starch (potatoes 15%, wheat 55%, corn 65%, and rice 75%). Commercial starch is a white powder.
Starch is a mixture of two polymers: amylose and amylopectin. Natural starches consist of about 10%–30% amylase and 70%–90% amylopectin. Amylose is a linear polysaccharide composed entirely of D-glucose units joined by the α-1,4-glycosidic linkages we saw in maltose (see part (a) in the figure below). Experimental evidence indicates that amylose is not a straight chain of glucose units but instead is coiled like a spring, with six glucose monomers per turn (see part (b) in the figure below). When coiled in this fashion, amylose has just enough room in its core to accommodate an iodine molecule. The characteristic blue-violet color that appears when starch is treated with iodine is due to the formation of the amylose-iodine complex. This color test is sensitive enough to detect even minute amounts of starch in solution.
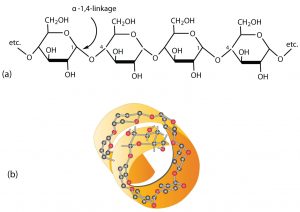
Amylopectin is a branched-chain polysaccharide composed of glucose units linked primarily by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds but with occasional α-1,6-glycosidic bonds, which are responsible for the branching. A molecule of amylopectin may contain many thousands of glucose units with branch points occurring about every 25–30 units (see figure below). The helical structure of amylopectin is disrupted by the branching of the chain, so instead of the deep blue-violet color amylose gives with iodine, amylopectin produces a less intense reddish brown.
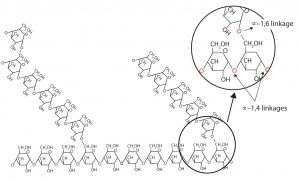
Dextrins are glucose polysaccharides of intermediate size. The shine and stiffness imparted to clothing by starch are due to the presence of dextrins formed when clothing is ironed. Because of their characteristic stickiness with wetting, dextrins are used as adhesives on stamps, envelopes, and labels; as binders to hold pills and tablets together; and as pastes. Dextrins are more easily digested than starch and are therefore used extensively in the commercial preparation of infant foods.
The complete hydrolysis of starch yields, in successive stages, glucose:
starch → dextrins → maltose → glucose
In the human body, several enzymes known collectively as amylases degrade starch sequentially into usable glucose units.
Glycogen
Glycogen is the energy reserve carbohydrate of animals. Practically all mammalian cells contain some stored carbohydrates in the form of glycogen, but it is especially abundant in the liver (4%–8% by weight of tissue) and in skeletal muscle cells (0.5%–1.0%). Like starch in plants, glycogen is found as granules in liver and muscle cells. When fasting, animals draw on these glycogen reserves during the first day without food to obtain the glucose needed to maintain metabolic balance.
About 70% of the total glycogen in the body is stored in muscle cells. Although the percentage of glycogen (by weight) is higher in the liver, the much greater mass of skeletal muscle stores a greater total amount of glycogen.
Glycogen is structurally quite similar to amylopectin, although glycogen is more highly branched (8–12 glucose units between branches) and the branches are shorter. When treated with iodine, glycogen gives a reddish brown color. Glycogen can be broken down into its D-glucose subunits by acid hydrolysis or by the same enzymes that catalyze the breakdown of starch. In animals, the enzyme phosphorylase catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen to phosphate esters of glucose.
Cellulose
Cellulose, a fibrous carbohydrate found in all plants, is the structural component of plant cell walls. Because the earth is covered with vegetation, cellulose is the most abundant of all carbohydrates, accounting for over 50% of all the carbon found in the vegetable kingdom. Cotton fibrils and filter paper are almost entirely cellulose (about 95%), wood is about 50% cellulose, and the dry weight of leaves is about 10%–20% cellulose. The largest use of cellulose is in the manufacture of paper and paper products. Although the use of noncellulose synthetic fibers is increasing, rayon (made from cellulose) and cotton still account for over 70% of textile production.
Like amylose, cellulose is a linear polymer of glucose. It differs, however, in that the glucose units are joined by β-1,4-glycosidic linkages, producing a more extended structure than amylose (part (a) of the figure below). This extreme linearity allows a great deal of hydrogen bonding between OH groups on adjacent chains, causing them to pack closely into fibers (part (b) of the figure below). As a result, cellulose exhibits little interaction with water or any other solvent. Cotton and wood, for example, are completely insoluble in water and have considerable mechanical strength. Because cellulose does not have a helical structure, it does not bind to iodine to form a colored product.
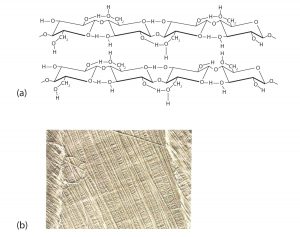
Cellulose yields D-glucose after complete acid hydrolysis, yet humans are unable to metabolize cellulose as a source of glucose. Our digestive juices lack enzymes that can hydrolyze the β-glycosidic linkages found in cellulose, so although we can eat potatoes, we cannot eat grass. The undigested cellulose in fibrous foods is passed through our digestive system as dietary fiber.
Unlike humans, certain microorganisms can digest cellulose because they make the enzyme cellulase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of cellulose. The presence of these microorganisms in the digestive tracts of herbivorous animals (such as cows, horses, and sheep) allows these animals to degrade the cellulose from plant material into glucose for energy. Termites also contain cellulase-secreting microorganisms and thus can subsist on a wood diet. This example once again demonstrates small changes in structure have huge implications for biochemical processes.
Concept Review Exercises
- What purposes do starch and cellulose serve in plants?
- What purpose does glycogen serve in animals?
- What monosaccharide is obtained from the hydrolysis of each carbohydrate?
- starch
- cellulose
- glycogen
- Indicate whether each polysaccharide is found in plants or mammals.
- starch
- cellulose
- glycogen
- Describe the similarities and differences between amylose and cellulose.
- Describe the similarities and differences between amylopectin and glycogen.
Solutions
- Starch is the storage form of glucose (energy) in plants, while cellulose is a structural component of the plant cell wall.
- Glycogen is the storage form of glucose (energy) in animals.
- What monosaccharide is obtained from the hydrolysis of each carbohydrate?
- glucose
- glucose
- glucose
- Indicate whether each polysaccharide is found in plants or mammals.
- plants
- plants
- animals
-
Amylose and cellulose are both linear polysaccharides of glucose units, but the glycosidic linkages between the glucose units differ. The linkages in amylose are α-1,4-glycosidic linkages, while the linkages in cellulose they are β-1,4-glycosidic linkages.
- Amylopectin and glycogen are both branched polysaccharides of glucose units, but glycogen is more branched than amylopectin. Both polysaccharides consist of linear chains of glucose linked by α-1,4-glycosidic linkages. The branches occur more often in glycogen and are connected to the linear chain by α-1,6-glycosidic linkages.
Attributions
This page is based on “Chemistry 2e” by Paul Flowers, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley, William R. Robinson, PhD, Openstax which is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/1-introduction
This page is based on “The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry” by David W Ball, John W Hill, Rhonda J Scott, Saylor which is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Access for free at http://saylordotorg.github.io/text_the-basics-of-general-organic-and-biological-chemistry/index.html

