Lesson 2: The Bench Vise
WORD LIST
|
1. drill |
to make a hole with a drill, to bore a hole. Example: Maria drilled a hole in the center of the gear. |
|
2. saw |
to cut with a saw. A saw is cutting tool that uses a blade with cutting teeth. Example: Paco, saw off a one-foot piece from that rough stock. |
|
3. file |
to smooth or grind a rough surface with a file. A file is a steel tool with rough surfaces for grinding and smoothing. Example: The robber filed the number off the engine. |
|
4. polish |
to smooth and make bright by rubbing. Example: Adolfo polishes the aluminum part until it shines. |
|
5. operation |
an act or method of doing something to make a finished part. Example: Cutting, drilling, and polishing are machine shop operations. |
|
6. lock |
a part that fastens something shut and prevents it from being opened. Example: Juana put a lock on the garage door. |
|
7. swivel |
a part that joins two other parts, but allows them to turn freely. Example: The swivel on the bench vise allows the machinist to turn the jaws of the vise in any direction. |
|
8. edge |
the line where something begins or ends; the border; the part farthest from the center. Example: Don’t put that can of paint near the edge of the table; it could get knocked over. |
|
9. attach |
to join, to fasten, to connect. Example: Clara attached the gear to the end of the shaft. |
|
10. hardened |
made harder than usual. Example: Steel can be hardened by heat and chemicals. |
Vocabulary Practice
BENCH VISE
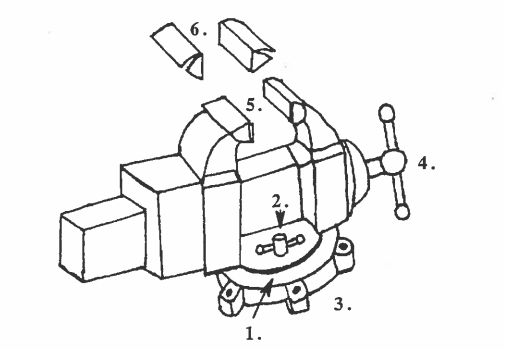
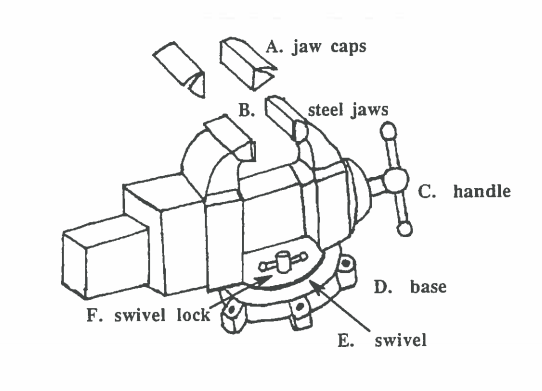
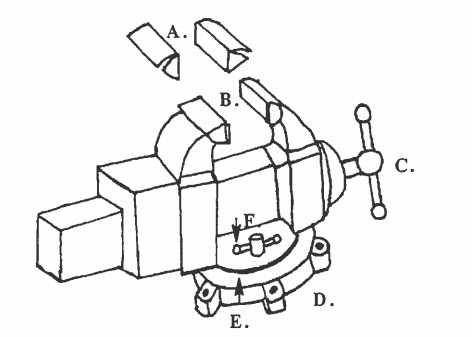
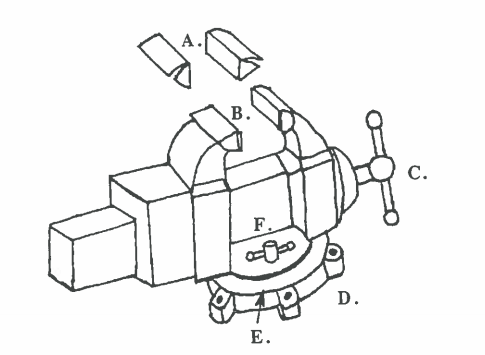
Before we being studying bench tools, let’s look at a tool that is not portable, the bench vise. It’s not portable because it’s attached to the bench. The purpose of the vise is to hold a workpiece tightly, while the machinist is working on it. The vise is usually fastened to the edge of the bench.
Often the vise has a swivel on the bottom. A swivel permits the vise to rotate (turn around) in any direction. When the machinist finds the correct position, they can lock the vise with the swivel lock.
The vise has hardened steel jaws to hold the workpiece. The vise handle is often used to tighten the jaws around the workpiece. Vise jaw caps fit over the jaws, when needed. The caps are made of softer metal like copper, brass, or aluminum. With the caps the vise will hold finished parts or soft materials without cutting into them or making marks.
When a workpiece is held tightly in the vise, a machinist can drill, saw, file, polish and do other operations to the workpiece. An operation is any work the machinist does to the workpiece, like drilling, cutting, polishing and sawing.
BENCH VISE vocabulary practice
BENCH VISE vocabulary practice
BENCH VISE vocabulary practice
BENCH VISE vocabulary practice
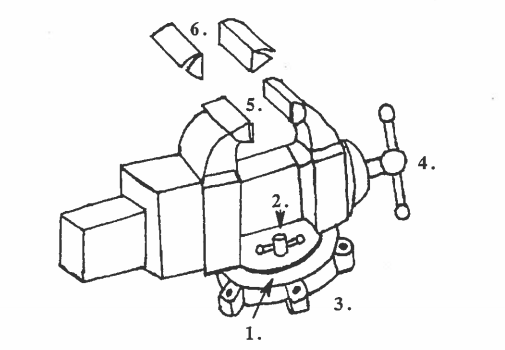
THE PURPOSE OF THE BENCH VISE
End of Lesson Questions
Part A: Answer the questions
Part B: Look at the picture. Listen to the words on the recording. Write the correct letters in the space below.
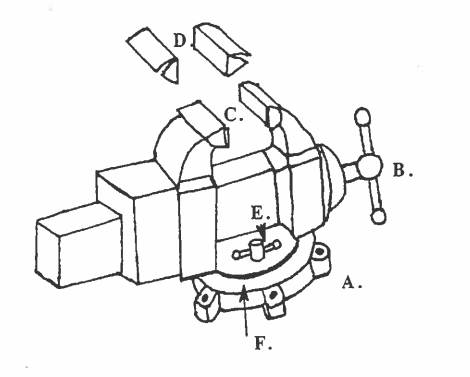
Part B: Look at the picture. Type the correct part name next to its number.