Lesson 3: Career Pathways for Machinists
Reading:
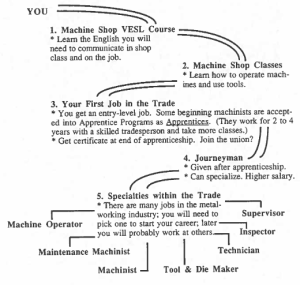
We sometimes talk about a career path; a career path is a road through life that a person can plan and take, in order to get better jobs and become more skilled. You are now thinking about a career in the metalworking industry. Let’s take a look at this path. It’s a path that many other machinists have walked before you.
Reading Technique: CORRECT SEQUENCE
When you read about steps in a correct order, you are reading a sequence of steps.
When you become a machinist, it will be necessary to do things in the correct order, in the right sequence. So let’s practice, and see if you can remember the correct sequence of steps along the Machinist’s Career Path.
Write the steps below in the correct order.
A CLOSER LOOK AT METALWORKING SPECIALTIES
Let’s look at the specialties (the different jobs) that a worker can choose in the metalworking trade. The work is changing each year, because machinists are finding new and better ways to do their work. Here are some of the jobs that a worker can go into now.
- Machine Operator:
- Sets up.
- Operates and adjusts machines.
- Uses tools and measuring instruments correctly.
- Reads and understands drawings.
- Maintenance Machinist:
-
- Repairs machines by replacing old parts with new ones.
- Takes care of machines and keeps them running.
- Moves machines and puts them in a new place.
- Sets up production lines.
- May work in a factory maintenance shop.
- Machinist:
-
- Operates all kinds of machines and uses machine tools.
- Knows and uses mathematics, welding, and computers.
- May work in a production shop, making parts.
- Tool and Die Maker:
-
- Makes tools that help the machinists do their work.
- Needs experience as a machinist before this specialty.
- Must be good in math, print reading, and design.
- Technician:
-
- Works with the engineers who design the machines and also with the machinists who makes them.
- Must be an excellent machinist before going to this job.
6. Inspector:
-
- Controls the quality of the finished parts that are made.
- Inspects (looks at carefully) the parts and measures them to see if the machinists have made them correctly.
7. Supervisor:
-
- Tells workers what jobs to do; checks to see that work is done correctly.
- Helps workers to learn on the job and to improve their work habits.
- Communicates with both managers and workers.
Print this worksheet: 1.3 Career worksheet
End-of-Lesson Questions

