G76 Threading Cycle
OBJECTIVES
After completing this unit, you should be able to:
- Identify and describe G76 Threading Cycle
- Calculate for K word used in G76
- Calculate for D word used in G76
- Selection number of passes for N word in G76
G76 Threading Cycle
Read this webpage from HAAS about G76 Threading Cycle, Multiple Pass (Group 00).
G76 is the automatic cycle for threading. Remember, the name of these automatic cycles in CNC codes is Canned Cycles.
Variable List:
X = minor diameter, d
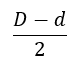
Z = length of thread, where D stops
K = radial thread height = (D – d) divided by 2. [K needs a radial value. The difference of diameters is split into two to get the radius.]
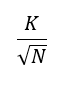
D = Depth of Cut. K is divided by the square root of N; where N is the Number of passes.
The deeper the cut, the greater the chip load on the cutting tool.
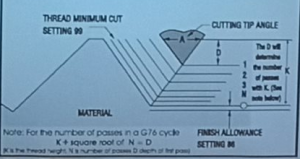
The first cut is shorter and deeper than the final cut.
The final cut is longer and not as deep as the first cut.
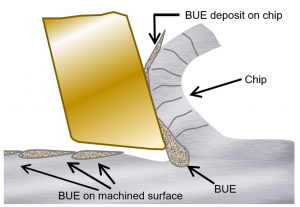
The increase in chip load causes Build Up Edge (BUE) on the cutting surface.
How do we determine the N–number of passes–for our calculations?
Look at the thread call out. Identify whether the thread is Coarse or Fine.
- Unified National Coarse (UNC)
- Unified National Fine (UNF)
As an introduction, choose from the following for N.
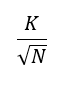
- Use 10, 12, or 15 passes for coarse threads
- Use 4 or 5 passes on fine threads

F = Pitch
Threading is the last step before we part workpiece off.
Calculation Steps:
|
 |
For example:
Step 1: 1 – 8 UNC 2A, 1″ long
Steps 2 & 3: major diameter is .9986. The minor diameter is .8492.
Step 4: X = .8492 (minor diameter)
Step 5: Z = 1.000 (length of thread]
Step 6: K = .9986 – .8492 = .1488. Divide by 2 = .0744
Step 7: This thread is coarse. Let’s choose 10 passes for N. 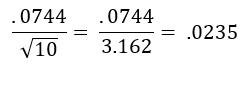
Step 8: D = .0235
Step 9: F = 1/8 = .125
Z = 1
K = .0744
D = .0235
F = .125
G76 Calculation
Thread Call out: 7/8 – 9 UNC 2A, 1″ long
Single line threading
On printout, the only thing given to you is thread callout
MHB
Look up minor dia
Radial thread height D-d/2
D passes depends on hardneess of material and coarse or fine of thread
e.g.
pic ¾-10 for thread callout
remember 2A is standard
D = .7482 -.7353
Mino: .6255
.005 less than major D
D = .745 Talk about this
It could be average . . . talk about range of Major D
Less amount of thread, rpm slower (under .1000)
Higher thread count, 32, 64, 80 rpm S1500
|
G28 T0303 (60 deg thread) G97 (not max rpm not use CSS) S700 M05 G54 G00 X Less amount of thread, rpm slower (under .1000) Higher thread count, 32, 64, 80 rpm S1500
X2.2, Z1.0 M08 |
Header |
|
Infeed, give cutter a start, need to start off part Need to know major D bring cutter .100 off part X2 for dia of part x.945 Z.2 (give it a little extra space to feed in before it starts to move G76 cycle) G76 X .6255 Z .950 K .0598 D .0173 F .100 For length Z, keep tool off the shoulder. Subtract .050 Length 1” – .050 for Z above K = math This is a big thread Coarse passes, on the final I will give you the number of passes . . . e.g. 12 passes D = practice calculator use Fairly big DOC. F picth 1/20 = .100 |
Body |
|
G00 Z1.0 M09 G28 M05 M30 |
Footer |

