31 Polymer Hardness Testing
The Shore durometer is a device for measuring the hardness of a material, typically of polymers.
Higher numbers on the scale indicate a greater resistance to indentation and thus harder materials. Lower numbers indicate less resistance and softer materials.
The term is also used to describe a material’s rating on the scale, as in an object having a “‘Shore durometer’ of 90.”
The scale was defined by Albert Ferdinand Shore, who developed a suitable device to measure hardness in the 1920s. It was neither the first hardness tester nor the first to be called a durometer (International Scientific Vocabulary duro- and -meter; attested since the 19th century), but today that name usually refers to Shore hardness; other devices use other measures, which return corresponding results, such as for Rockwell hardness.
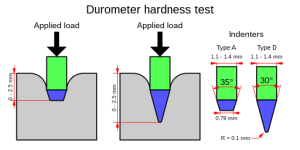
Durometer, like many other hardness tests, measures the depth of an indentation in the material created by a given force on a standardized presser foot. This depth is dependent on the hardness of the material, its viscoelastic properties, the shape of the presser foot, and the duration of the test. ASTM D2240 durometers allows for a measurement of the initial hardness, or the indentation hardness after a given period of time. The basic test requires applying the force in a consistent manner, without shock, and measuring the hardness (depth of the indentation). If a timed hardness is desired, force is applied for the required time and then read. The material under test should be a minimum of 6 mm (0.25 inches) thick.
Video
Watch this 2:30 video How to Measure Shore A (Hardness Scale) With a Durometer + Examples – YouTube by Jaycon, December 9, 2020.
Derived from Shore durometer – Wikipedia. Accessed and available online 23 January 2024.

