29 Scratch and Spark Testing
Scratch hardness refers to the hardness of a material in terms of resistance to scratches and abrasion by a harder material forcefully drawn over its surface.
Scratch hardness test or scratch test refers to any of a number of methods of measuring scratch hardness. Resistance to abrasion is less affected by surface variations than indentation methods. Scratch hardness is measured with a sclerometer.
Attempting to scratch a surface to test a material is a very old technique. The first scientific attempt to quantify materials by scratch tests was by mineralogist Friedrich Mohs in 1812, who established the Mohs scale. The Mohs scale is based on relative scratch hardness of different materials; with talc assigned a value of 1 and diamond assigned a value of 10. Mohs’s scale had two limitations: it was not linear, and most modern abrasives fall between 9 and 10; so, later scientists attempted to increase resolution at the harder end of the scale.
Raymond R. Ridgway, a research engineer at the Norton Company, modified the Mohs scale by giving garnet a hardness of 10 and diamond a hardness of 15. Charles E. Wooddell, working at the Carborundum Company, extended the scale further by using resistance to abrasion, and extrapolating the scale based on 7 for quartz and 9 for corundum, resulting in a value of 42.4 for South American brown diamond bort.
There is a linear relationship between cohesive energy density (lattice energy per volume) and Wooddell wear resistance, occurring between corundum (H=9) and diamond (H=42.5).
Mohs
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. This technique is very old. Theophrastus writes about it in his treatise On Stones, c. 300 BC, followed by Pliny the Elder in his Naturalis Historia, c. AD 77. In modern times, it is called a qualitative method because it relies on scratch marks and not measurement.
There are 10 different minerals or stones in a Mohs kit. Each stone is given a number from softest to hardest. The stone that scratches the metal is the number that metal is given, from 1 to 10. This is called an ordinal scale. The scale was introduced in 1812 by the German geologist and mineralogist Friedrich Mohs, in his book “Versuch einer Elementar-Methode zur naturhistorischen Bestimmung und Erkennung der Fossilien”.
Each of the ten hardness values in the Mohs scale is represented by a reference mineral, most of which are widespread in rocks.
The Mohs scale is an ordinal scale. For example, corundum (9) is twice as hard as topaz (8), but diamond (10) is four times as hard as corundum. The table below shows the comparison with the absolute hardness measured by a sclerometer, with pictorial examples.
| Mohs hardness | Reference mineral | Chemical formula | Absolute hardness | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Talc | Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 | 1 |  |
| 2 | Gypsum | CaSO4·2H2O | 2 |  |
| 3 | Calcite | CaCO3 | 14 |  |
| 4 | Fluorite | CaF2 | 21 |  |
| 5 | Apatite | Ca5(PO4)3(OH−,Cl−,F−) | 48 |  |
| 6 | Orthoclase feldspar | KAlSi3O8 | 72 |  |
| 7 | Quartz | SiO2 | 100 |  |
| 8 | Topaz | Al2SiO4(OH−,F−)2 | 200 |  |
| 9 | Corundum | Al2O3 | 400 |  |
| 10 | Diamond | C | 1500 |  |
| Source: Mohs scale – Wikipedia |
The Mohs scale is useful for identification of minerals in the field but is not an accurate predictor of how well materials endure in an industrial setting.
Video
Watch this 2:20 video The Mohs Scale of Hardness Explained by MooMooMath and Science, Aril 4, 2020.
File Scratch Testing
A magnet cannot identify the difference between low-carbon, medium-carbon, or high-carbon steels. Low-carbon and medium-carbon steels can sometimes be identified from the other the higher types of carbon steels by using a file or chisel. A file or chisel intended for use on steel will bite easily into low-carbon and medium-carbon steel to remove metals chips.
Apply pressure with the file to the unknown metal on the forward stroke of the file. The file or chisel will remove ships with ease with lower carbon content. Chips will be filed or chiseled off the difficulty or not at all with higher carbon content steels.
Video
Watch this 10:12 video which includes file scratch examples. Identifying metals only using a file and a magnet, by Ben Houghton, April 3, 2017.
Spark Testing
Spark testing is a method of determining the general classification of ferrous materials. It normally entails taking a piece of metal, usually scrap, and applying it to a grinding wheel in order to observe the sparks emitted. These sparks can be compared to a chart or to sparks from a known test sample to determine the classification. Spark testing also can be used to sort ferrous materials, establishing the difference from one another by noting whether the spark is the same or different.


Spark testing is used because it is quick, easy, and inexpensive. Moreover, test samples do not have to be prepared in any way, so, often, a piece of scrap is used. The main disadvantage to spark testing is its inability to identify a material positively; if positive identification is required, chemical analysis must be used. The spark comparison method also damages the material being tested, at least slightly.
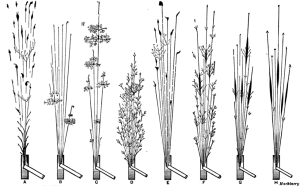
(B) Mild steel
(C) Steel with 0.5 to 0.85% carbon
(D) High-carbon tool steel
(E) High-speed steel
(F) Manganese steel
(G) Mushet steel
(H) Special magnet steel
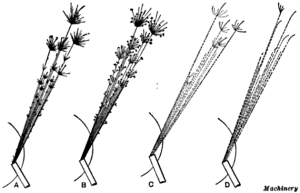
(A) High-carbon steel
(B) Manganese steel
(C) Tungsten steel
(D) Molybdenum steel
Original Source: Oberg, Erik; Jones, Franklin Day (1918), Iron and Steel (1st ed.), The Industrial Press.
Videos
Watch this 6:18 video SPARK TEST FOR METAL IDENTIFICATION – DETERMINE THE METAL TIPS TRICKS AND ADVICE by Longevity Welding, February 26, 2013.
Watch through this short presentation about using a spark test to identify metals: Spark Testing of Materials – Wisc-Online OER
Watch this 12:19 video which includes slow motion photography of various sparks. How to Spark Test Metals. Surprising Slow Motion Footage FarmCraft101 by FarmCraft101, December 13, 2019.
Derived from Scratch hardness – Wikipedia and Mohs scale – Wikipedia available and accessed online 1 February 2024.
Text source: Spark testing – Wikipedia. Accessed and available 23 January 2024.
Available and accessed at Spark Testing of Materials – Wisc-Online OER. 19 January 2024.

