12 Electric Furnace
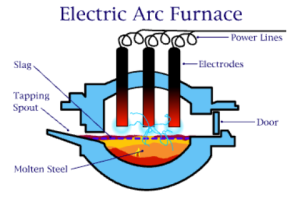
The second way to refine the pig iron into steel is called the electric arc furnace (EAF) steel making process.
In this process, the amount of carbon is regulated by exposing the pig iron an electric arc. The arc is generated by electrodes in the oven which are placed on opposite sides of the molten.
An electric arc furnace is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc.
Industrial arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one-ton capacity (used in foundries for producing cast iron products) up to about 400-ton units used for secondary steelmaking. Arc furnaces used in research laboratories and by dentists may have a capacity of only a few dozen grams. Industrial electric arc furnace temperatures can reach 1,800 °C (3,300 °F), while laboratory units can exceed 3,000 °C (5,400 °F).
In electric arc furnaces, the charged material (the material entered into the furnace for heating, not to be confused with electric charge) is directly exposed to an electric arc, and the current from the electrode terminals passes through the charged material. Arc furnaces differ from induction furnaces, in which the charge is heated instead by eddy currents.
Video explanation
Watch this 5:32 video, “A Detailed Explanation of the Electric Arc Explanation–What It Is and How It Works” by James Sword Research (2022)
Advantages for steelmaking
The use of EAFs allows steel to be made from a 100% scrap metal feedstock. This greatly reduces the energy required to make steel when compared with primary steelmaking from ores.
Another benefit is flexibility: while blast furnaces cannot vary their production by much and can remain in operation for years at a time, EAFs can be rapidly started and stopped, allowing the steel mill to vary production according to demand.
Although steelmaking arc furnaces generally use scrap steel as their primary feedstock, if hot metal from a blast furnace or direct-reduced iron is available economically, these can also be used as furnace feed.
As EAFs require large amounts of electrical power, many companies schedule their operations to take advantage of off-peak electricity pricing.
A typical steelmaking arc furnace is the source of steel for a mini-mill, which may make bars or strip product. Mini-mills can be sited relatively near the markets for steel products, so the transport requirements are less than for an integrated mill, which would commonly be sited near a harbor for better access to shipping.
Electric arc furnace steelmaking results in lower carbon dioxide emissions of around 0.6 ton CO2 per ton of steel produced, which is significantly lower than the conventional production route via blast furnaces and the basic oxygen furnace.
Safety Tip
Read this Safety Bulletin from the
Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA)
Carbon Monoxide Explosion Hazards in Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking Operations
Derived from: Electric arc furnace – Wikipedia Available and accessed 6 February 2024 and The Virtual Machine Shop (2011) at http://jjjtrain.com/3engineering/5eng_metallurgy/eng_metallurgy_12.html retrieved by the WayBack Machine internet archive 16 January 2024.

