38 Angles
History of Angles
It all starts with the circle.
In the circle below, a line segment starts at the center of the circle and ends on the edge.
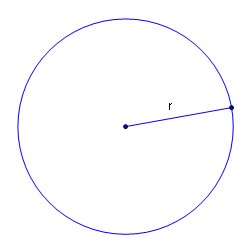
This distance from the center to any point on the edge of the circle is the radius. Notice the little “r” above the line that stands for radius.
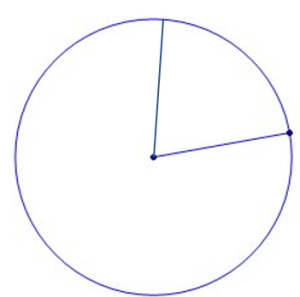
A circle with two radii lines has some space between the two lines. The measurement of that space is an angle. It is measured in degrees.
Vocabulary: Read the definitions for the following words.
Practice typing and spelling the new vocabulary words

King Nebuchabnezzar of ancient Babylonia lived from 605-562 BCE. During this time, the measurement of the circle was established to be 360 degrees.
One explanation for dividing the circle into 360 is that the Babylonians calculated the earth going around the sun in 360 days.
In modern times, angles may also be measured in radians.
Watch this 4:39 video The Origin of Degrees and Radians by Beau Janzen, May 12, 2024.
We will only be practicing with degrees in this chapter.
Euclid wrote about angles. He wrote the following observation.
1.) All right angles are congruent.
This is easy. Right angles are made with a horizontal line and vertical line crossing it. They are perpendicular lines going in opposite directions. The corner the lines make when they cross is a “right triangle”. It is always 90 degrees. Congruent means the measurement is the same. Therefore, all right triangles are 90 degrees.

